Artificial Intelligence
Northeastern University Library (NUL) stands at the forefront of digital transformation in teaching, learning, research, and scholarly communication. NUL envisions a future where artificial intelligence serves as a catalyst for intellectual discovery, enhancing scholarly pursuits while deeply rooted in core library values of accessibility, equity, and critical inquiry, and truth-seeking. Through strategic external partnerships and interdisciplinary collaborations, NUL is pioneering AI integrations across numerous domains:
Research & Discovery
Investment in AI-powered information resources
Scite-AI: An AI-powered research platform that analyzes and provides citation context for scientific papers. Scite is built on a database of 1.2 billion citations from 200 million full-text peer-reviewed articles.*
Scopus AI: Enter a natural language query and receive results from the largest multidisciplinary abstract and citation database including graphical representations showing connections among keywords, pointers to influential papers, and suggested related queries to further your research.
Keeping track of AI Innovations
The Information: provides in-depth, breaking news articles about the global technology industry– including the areas of artificial intelligence, venture capital, crypto, start-ups, private equity in the technology space. Enter your @northeastern.edu email address to link your Northeastern credentials.
Scholarly Journals
The Library provides access to numerous journals focused on Artificial Intelligence, including:
- Artificial Intelligence (Elsevier)
- Artificial Intelligence in Engineering (Elsevier)
- Artificial Intelligence Review (Springer)
- Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (Burgberlag)
- Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence (Oxford)

Teaching & Learning
Library AI Modules
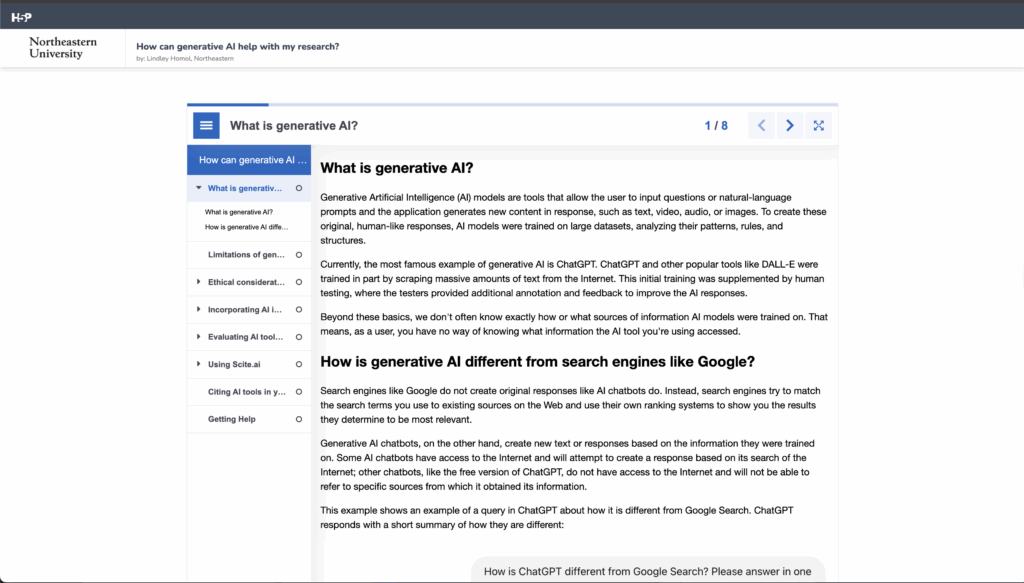
Librarians created a multi-module learning object that introduces generative AI, explains limitations of generative AI, delves into ethical considerations, helps students evaluate tools and incorporate AI into the research process, and provides tips on using library-licensed AI platforms.
Course Support
Research and Instruction Librarians can address generative AI in the context of information literacy as is relevant to your course and/or assignments to help prepare students to work with the ongoing evolution of GenAI tools. Librarians focus their learning objectives on skills, such as prompt generation and evaluation, that are transferable across Northeastern-licensed research databases and tools.
AI in the Library
Grant Funded Initiatives in AI
NUL is a chief collaborator on a grant from the Authors Alliance, supported by the Mellon Foundation: Developing a public-interest training commons of books. The grant seeks to develop an actionable plan for a public-interest book training commons for artificial intelligence, considering various legal pathways, roles for different stakeholders, and potential governance models.
Digitization & Metadata Creation

Using Whisper to generate accessible captions for streaming audio and video resources

Leveraging the Gemini API’s vision capabilities to create titles and abstracts for photographs

Producing searchable text documents through optical character recognition with Tesseract, Adobe, and Abbyy FineReader.
AI Interest Group
NUL staff engage in ongoing learning and research to develop expertise that supports the university community and advances knowledge in the library and information science discipline. Staff regularly attend AI-focused training sessions and conferences, and contribute to the scholarly literature by writing articles and blog posts exploring AI applications in library practice. In 2024, NUL established an artificial intelligence interest group to examine emerging AI trends and comprehend ways in which AI can transform libraries, serving as a valuable forum through which library staff can learn and be inspired to integrate AI into their work.
*See “scite: A smart citation index that displays the context of citations and classifies their intent using deep learning,” published in Quantitative Science Studies, 2021.